
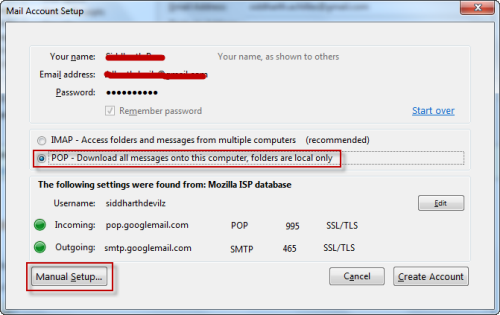
Thunderbird will verify your settings to ensure they’re correct. * In the Port drop-down menu, select 465.ħ) In the Mail Account Setup window, click the Re-Test button. * Enter your outgoing server name in the Server Hostname field. * Leave the Authentication field set to Autodetect.Ħ) Set up the Outgoing fields as follows: * In the Port drop-down menu, select 993 for IMAP and 995 for POP3. * Enter your incoming server name in the Server Hostname field. * Select either IMAP or POP3 from the first dropdown menu. * Your incoming (POP3 or IMAP) server name.ĥ) Set up the Incoming fields as follows: If Thunderbird can’t find your email settings automatically, you’ll be prompted to enter the following information: Click Continue.Ĥ) Thunderbird tries to automatically find your email settings in its database of email servers. Enter your name, the email address for the account you wish to set up, and the password used for your email account. Your Outgoing (SMTP) server name, provided in your Welcome email.ġ) Click the Tools menu and select Account Settings to open the Account Settings window.Ģ) In the Account Settings window, open the Account Actions menu and select Add Account.ģ) The Mail Account Setup window appears.Your Incoming (POP3) server name, provided in your Welcome email.Choose IMAP to leave your email on the server – a great choice if you travel often and need to access email from different devices and geographical locations, or when you don’t want to take up space on your computer.įor this article, we’ll be using Thunderbird 52.0.
#SET THUNDERBIRD FOR POP EMAIL FOR GMAIL SOFTWARE#
Choose POP3 download email to your computer every time (you can also set your email software to leave a copy of messages on the server if necessary).The difference between POP3 and IMAP is where your email is stored: Using SSL encrypts your email data and prevents third parties from viewing your messages. If you’re concerned about the security of the information you send and receive in email, configure your POP3 or IMAP account with SSL (Secure Sockets Layer).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
